Featured Article

More than 90% of the compounds that enter clinical trials fail to demonstrate sufficient safety and efficacy to gain regulatory approval. Most of this failure is due to the limited predictive value of preclinical models of disease, and our continued ignorance regarding the consequences of perturbing specific targets over long periods of time in humans. ‘Experiments of nature’ — naturally occurring mutations in humans that affect the activity of a particular protein target or targets — can be used to estimate the probable efficacy and toxicity of a drug targeting such proteins, as well as to establish causal rather than reactive relationships between targets and outcomes. Here, we describe the concept of dose–response curves derived from experiments of nature, with an emphasis on human genetics as a valuable tool to prioritize molecular targets in drug development. We discuss empirical examples of drug–gene pairs that support the role of human genetics in testing therapeutic hypotheses at the stage of target validation, provide objective criteria to prioritize genetic findings for future drug discovery efforts and highlight the limitations of a target validation approach that is anchored in human genetics.
All Publications

Human genetics for target validation in drug discovery
August 2013
Validating therapeutic targets through human genetics, Robert M. Plenge, Edward M. Scolnick and David Altshuler. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2013 Aug;12(8):581-94. doi: 10.1038/nrd4051. Epub 2013 Jul 19. PMID: 23868113
We describe a strategy to use human genetics as a powerful tool to validate therapeutic targets for drug discovery. We frame the concept of “genotype-phenotype dose-response curves”.
View article PDF
Genes to drugs in RA
May 2013
Human genetics in rheumatoid arthritis guides of high-throughput drug screen of the CD40 signaling pathway, Li G, Diogo D, Wu D, Spoonamore J, Dancik V, Franke F, Kurreeman F, Rossin EJ, Duclos G, Hartland C, Zhou X, Li K, Liu J, De Jager PL, Siminovitch KA, Zhernakova A, Raychaudhuri S, Bowes J, Eyre S, Padyukov L, Gregersen PK, Worthington J, Rheumatoid Arthritis Consortium International (RACI), Gupta N, Clemons PA, Stahl E, Tolliday N, Plenge RM. PLoS Genetics. 2013 May, in progress.
We demonstrate how to leverage human genetics for drug discovery. Genetics of risk of RA points to a pathway (CD40-CD40L signaling) and a HTS assay (NF-kB luciferase-reporter in a B cell line), which was used in a pilot small molecule drug screen at the Broad Institute.

RA Responder Challenge
May 2013
Crowdsourcing genetic prediction of clinical utility in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Responder Challenge, Plenge RM, Greenberg JD, Mangravite LM, Derry JM, Stahl EA, Coenen MJ, Barton A, Padyukov L, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Mariette X, Moreland LW, Bridges SL Jr, de Vries N, Huizinga TW, Guchelaar HJ; International Rheumatoid Arthritis Consortium (INTERACT), Friend SH, Stolovitzky G. Nat Genet. 2013 Apr 26;45(5):468-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.2623. PMID: 23619782.
We announce a new collaboration between PGRN, Sage Bionetworks, DREAM, the Arthritis Foundation, CORRONA, and others. The goal is to use crowdsourcing to identify genetic predictors of response to anti-TNF therapy in RA.

anti-TNF GWAS in RA
March 2013
Genome-Wide Association Study and Expression Analysis Identifies CD84 as a Predictor of Response to Etanercept Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Cui J, Stahl EA, Saevarsdottir S, Miceli C, Diogo D, Trynka G, Raj T, Umiċeviċ-Mirkov M, Canhao H, Ikari K, Terao C, Okada Y, Wedrén S, Askling J, Yamanaka H, Momohara S, Taniguchi A, Ohmura K, Matsuda F, Mimori T, Gupta N, Kuchroo M, Morgan AW, Isaacs JD, Wilson AG, Hyrich KL, Herenius M, Doorenspleet ME, Tak PP, Crusius JBA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Wolbink GT, van Riel PLCM, van de Laar M, Guchelaar HJ, Shadick NA, Allaart CF, Huizinga TWJ, Toes REM, Kimberly RP, Bridges Jr SL, Criswell LA, Moreland LW, Fonseca JE, de Vries N, Stranger BE, De Jager PL, Raychaudhuri S, Weinblatt ME, Gregersen PK, Mariette X, Barton A, Padyukov L, Coenen MJH, Karlson EW, Plenge RM. PLoS Genetics. published 28 Mar 2013.
We found evidence that a common, non-coding variant near the CD84 gene influences response to one anti-TNF drug (etanercept). The same variant is an eQTL for the CD84 gene.
View article PDF
autoantigen discovery with PhIP-seq
March 2013
PhIP-seq characterization of autoantibodies from patients with multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, Larman HB, Laserson U, Querol L, Verhaeghen K, Solimini NL, Xu GJ, Klarenbeek PL, Church GM, Hafler DA, Plenge RM, Nigrovic PA, De Jager PL, Weets I, Martens GA, O’Connor KC, Elledge SJ. J Autoimmun. 2013 Mar 13. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23497938
In collaboration with the Elledge lab, we performed a genome-wide search for autoantigens in patients with autoimmune disease.

EMR and IBD – depression and anxiety
January 2013
Similar Risk of Depression and Anxiety Following Surgery or Hospitalization for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, Ananthakrishnan AN, Gainer VS, Cai T, Perez RG, Cheng SC, Savova G, Chen P, Szolovits P, Xia Z, De Jager PL, Shaw S, Churchill S, Karlson EW, Kohane I, Perlis RH, Plenge RM, Murphy SN, Liao KP. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan 22. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2012.471. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23337479
IBD-related surgery or hospitalization is associated with a significant risk for depression and anxiety, with a similar magnitude of risk in both diseases.
View article PDF
Sequencing and rare variants in RA
January 2013
Rare, Low-Frequency, and Common Variants in the Protein-Coding Sequence of Biological Candidate Genes from GWAS Contribute to Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Diogo D, Kurreeman F, Stahl EA, Liao KP, Gupta N, Greenberg JD, Rivas MA, Hickey B, Flannick J, Thomson B, Guiducci C, Ripke S, Adzhubey I, Barton A, Kremer JM, Alfredsson L; Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America; Rheumatoid Arthritis Consortium International, Sunyaev S, Martin J, Zhernakova A, Bowes J, Eyre S, Siminovitch KA, Gregersen PK, Worthington J, Klareskog L, Padyukov L, Raychaudhuri S, Plenge RM. Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Jan 10;92(1):15-27. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PMID: 23261300
We provide evidence that protein-coding variants from GWAS identified by GWAS contribute to risk of RA independent from non-coding variants discovered by GWAS. The same approach can be used to identify an allelic series that could be useful in identifying drug targets.

EMR and IBD – surgery and psychiatric disease
January 2013
Psychiatric co-morbidity is associated with increased risk of surgery in Crohn’s disease, Ananthakrishnan AN, Gainer VS, Perez RG, Cai T, Cheng SC, Savova G, Chen P, Szolovits P, Xia Z, De Jager PL, Shaw SY, Churchill S, Karlson EW, Kohane I, Perlis RH, Plenge RM, Murphy SN, Liao KP. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Feb;37(4):445-54. doi: 10.1111/apt.12195. Epub 2013 Jan 7. PMID: 23289600
Depressive disorder or generalised anxiety is associated with a modestly increased risk of surgery in patients with Crohn’s disease. Interventions addressing this may improve patient outcomes.

GWAS on uric acid levels
January 2013
Genome-wide association analyses identify 18 new loci associated with serum urate concentrations, Köttgen A, Albrecht E, Teumer A, Vitart V, Krumsiek J, Hundertmark C, Pistis G, Ruggiero D, O’Seaghdha CM, Haller T, Yang Q, Tanaka T, Johnson AD, Kutalik Z, Smith AV, Shi J, Struchalin M, Middelberg RP, Brown MJ, Gaffo AL, Pirastu N, Li G, Hayward C, Zemunik T, Huffman J, Yengo L, … Bochud M, Gieger C.. Nat Genet. 2013 Feb;45(2):145-54. doi: 10.1038/ng.2500. Epub 2012 Dec 23. PMID: 23263486
New candidate genes for serum urate concentration highlight the importance of metabolic control of urate production and excretion, which may have implications for the treatment and prevention of gout.
View article PDF
GWAS of response to anti-TNF therapy
December 2012
Genome-wide association analysis of anti-TNF drug response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Umicevic Mirkov M, Cui J, Vermeulen SH, Stahl EA, Toonen EJ, Makkinje RR, Lee AT, Huizinga TW, Allaart R, Barton A, Mariette X, Miceli CR, Criswell LA, Tak PP, de Vries N, Saevarsdottir S, Padyukov L, Bridges SL, van Schaardenburg DJ, Jansen TL, Dutmer EA, van de Laar MA, Barrera P, Radstake TR, van Riel PL, Scheffer H, Franke B, Brunner HG, Plenge RM, Gregersen PK, Guchelaar HJ, Coenen MJ. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Dec 11. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23233654
Led by our colleague Dr. Marieke Coenen in the Netherlands, this is a GWAS of response to anti-TNF therapy in the DREAM cohort.
View article PDF
Autoantibodies and autoimmune risk alleles
December 2012
Autoantibodies, autoimmune risk alleles and clinical associations in rheumatoid arthritis cases and non-RA controls in the electronic medical records. Liao KP, Kurreeman F, Li G, Duclos G, Murphy S, P RG, Cai T, Gupta N, Gainer V, Schur P, Cui J, Denny JC, Szolovits P, Churchill S, Kohane I, Karlson EW, Plenge RM. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Dec 10. doi: 10.1002/art.37801. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23233247
We used i2b2 samples to demonstrate that autoimmune risk alleles influence the production of clinical autoantibodies (ANA, TPO, CCP, tTP) in both RA cases and non-RA controls.
View article PDF
NF-kB pathway and RA
December 2012
Identification of the NF-κB activating protein-like locus as a risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis, Xie G, Lu Y, Sun Y, Zhang SS, Keystone EC, Gregersen PK, Plenge RM, Amos CI, Siminovitch KA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Dec 6. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23223422
Led by our colleague Dr. Kathy Siminovich, our study provides evidence that common variants at the NKAPL gene locus confers risk of RA. Together with previous studies, this provides further evidence of the role of the NF-kB pathway in genetic risk of RA.

The iChip manuscript
December 2012
High-density genetic mapping identifies new susceptibility loci for rheumatoid arthritis. Eyre S, Bowes J, Diogo D, Lee A, Barton A, Martin P, Zhernakova A, Stahl E, Viatte S, McAllister K, Amos CI, Padyukov L, Toes RE, Huizinga TW, Wijmenga C, Trynka G, Franke L, Westra HJ, Alfredsson L, Hu X, Sandor C, de Bakker PI, Davila S, Khor CC, Heng KK, Andrews R, Edkins S, Hunt SE, Langford C, Symmons D; Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Concannon P, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Rich SS, Deloukas P, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Arlsetig L, Martin J, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Plenge RM*, Raychaudhuri S*, Klareskog L*, Gregersen PK*, Worthington J*. Nat Genet. 2012 Dec;44(12):1336-40. PMID: 23143596 *contributed equally
The “iChip” manuscript – we use data from Illumina’s Immunochip (iChip) to discover 14 new RA risk loci, as well as fine-map existing risk loci. One new RA risk locus is contains the gene IL6R (the protein product of IL6R is the target of the drug tocilizumab), which further emphasizes that concept genetics can identify drug targets.

A new method for association studies
November 2012
Informed conditioning on clinical covariates increases power in case-control association studies, Zaitlen N, Lindström S, Pasaniuc B, Cornelis M, Genovese G, Pollack S, Barton A, Bickeböller H, Bowden DW, Eyre S, Freedman BI, Friedman DJ, Field JK, Groop L, Haugen A, Heinrich J, Henderson BE, Hicks PJ, Hocking LJ, Kolonel LN, Landi MT, Langefeld CD, Le Marchand L, Meister M, Morgan AW, Raji OY, Risch A, Rosenberger A, Scherf D, Steer S, Walshaw M, Waters KM, Wilson AG, Wordsworth P, Zienolddiny S, Tchetgen ET, Haiman C, Hunter DJ, Plenge RM, Worthington J, Christiani DC, Schaumberg DA, Chasman DI, Altshuler D, Voight B, Kraft P, Patterson N, Price AL PLoS Genet. 2012 Nov;8(11):e1003032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003032. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PMID: 23144628
Led by Noah Zaitlen in Alkes Price’s lab, this study describes a new method for performing genetic tests of association that includes clinical data.
View article PDF
Candidate gene study in vasculitis
October 2012
Meta-analysis in granulomatosis with polyangiitis reveals shared susceptibility loci with rheumatoid arthritis, Chung SA, Xie G, Roshandel D, Sherva R, Edberg JC, Kravitz M, Dellaripa PF, Hoffman GS, Mahr AD, Seo P, Specks U, Spiera RF, William St Clair E, Stone JH, Plenge RM, Siminovitch KA, Merkel PA, Monach PA. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Oct;64(10):3463-71. PMID: 22508400
Led by Sharon Chung (UCSF) and Paul Monach (Boston University), we demonstrate shared genetic risk factors between patients with vasculitis and RA.
View article PDF
Candidate gene study of response to anti-TNF therapy
September 2012
Association of Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Alleles with Response to Anti-TNF Biologics: Results from the CORRONA Registry and Meta-analysis, Pappas DA, Oh C, Plenge RM, Kremer JM, Greenberg JD. Inflammation. 2012 Sep 25. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 23007924
Led by Jeff Greenberg and colleagues at CORRONA, we tested RA risk alleles for association with response to anti-TNF therapy.
View article PDF
Japanese GWAS of RA risk
May 2012
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies multiple novel loci associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population. Okada Y, Terao C, Ikari K, Kochi Y, Ohmura K, Suzuki A, Kawaguchi T, Stahl EA, Kurreman F, Nishida N, Ohmiya H, Myouzen K, Takahashi M, Sawada T, Nishioka Y, Yukioka M, Matsubara T, Wakitani S, Teshima R, Tohma S, Takasugi K, Shimada K, Murasawa A, Honjo S, Matsuo K, Tanaka H, Tajima K, Suzuki T, Iwamoto T, Kawamura Y, Tanii H, Okazaki Y, Sasaki T, Gregersen PK, Padyukov L, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Lathrop M, Taniguchi A, Takahashi A, Tokunaga K, Kubo M, Nakamura Y, Kamatani N, Mimori T, Plenge RM, Yamanaka H, Shigeki Momohara S, Yamada R, Matsuda F, and Yamamoto K. Nat Genet. 2012;44(5):511-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.2231. PMID: 22446963.
This study represents the largest GWAS among individuals of Japanese ancestry, and further demonstrates the genetic overlap between RA patients of Asian and European ancestry.
View article PDF
i2b2 paper on IBD
April 2012
Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Ananthakrishnan AN, Guzman-Perez R, Gainer V, Cai T, Churchill S, Kohane I, Plenge RM, Murphy S. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Apr;35(7):789-95. PMID: 22360370
Using EMR data in a virtual cohort of IBD patients, we identify clinical predictors of severe gastrointestinal infection.
View article PDF
Polygenic modeling of complex traits
March 2012
Bayesian inference reveals polygenic architecture of four common disease, Stahl EA, Wegmann D, Kraft P, Chen R, Kallberg H, Kurreeman FAS, Gregersen PK, Alfredsson L, Siminovitch KA, Worthington K, de Bakker PIW, Raychaudhuri S*, Plenge RM*. Nat Genet. 2012 Mar 25;44(5):483-9. PMID: 22446960. * contributed equally
Our “polygenic architecture” manuscript – we use GWAS data to demonstrate that risk of four common diseases (RA, celiac disease, myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes) is best explained by a mixture of both common and rare variants.
View article PDF
Multi-ethnic genetic study of RA risk
March 2012
Use of a Multiethnic Approach to Identify Rheumatoid-Arthritis-Susceptibility Loci, 1p36 and 17q12, Kurreeman FA, Stahl EA, Okada Y, Liao K, Diogo D, Raychaudhuri S, Freudenberg J, Kochi Y, Patsopoulos NA, Gupta N; CLEAR investigators, Sandor C, Bang SY, Lee HS, Padyukov L, Suzuki A, Siminovitch K, Worthington J, Gregersen PK, Hughes LB, Reynolds RJ, Bridges SL Jr, Bae SC, Yamamoto K, Plenge RM. Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Mar 9;90(3):524-32. PMID: 22365150
Using samples from i2b2, CLEAR (African Americans), Japan, and Korea, we demonstrate that a multi-ethnic approach is a power strategy to discover new RA risk loci.
View article PDF
EMR portability
February 2012
Portability of an algorithm to identify rheumatoid arthritis in electronic health records. Carroll RJ, Thompson WK, Eyler AE, Mandelin AM, Cai T, Zink RM, Pacheco JA, Boomershine CS, Lasko TA, Xu H, Karlson EW, Perez RG, Gainer VS, Murphy SN, Ruderman EM, Pope RM, Plenge RM, Kho AN, Liao KP, Denny JC. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012 Feb 28. PMID: 22374935
We demonstrate portability of our EMR algorithm to define RA virtual cohorts across institutions.
View article PDF
New HLA model of RA risk
January 2012
Five amino acids in three HLA proteins explain most of the association between MHC and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Raychaudhuri S, Sandor C, Stahl EA, Freudenberg J, Lee HS, Jia X, Alfredsson L, Padyukov L, Klareskog L, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Bae SC, Plenge RM, Gregersen PK, de Bakker PI. Nat Genet. 2012 Jan 29;44(3):291-6. PMID: 22286218
We refine the “shared epitope” hypothesis, demonstrating that amino acids in the binding groove of three different HLA proteins (class I and class II) confer risk of RA.
View article PDF
Genetic risk score in RA
September 2011
Genetic risk score predicting risk of rheumatoid arthritis phenotypes and age of symptom onset. Chibnik LB, Keenan BT, Cui J, Liao KP, Costenbader KH, Plenge RM, Karlson EW. PLoS One. 6(9):e24380. Epub 2011 Sep 12. PMID: 21931699
We show that a genetic risk score (GRS) for RA risk influences other phenotypes, too.
View article PDF
TAGAP and risk of RA
June 2011
Fine mapping the TAGAP risk locus in rheumatoid arthritis. Chen R, Stahl EA, Kurreeman FA, Gregersen PK, Siminovitch KA, Worthington J, Padyukov L, Raychaudhuri S, Plenge RM. Genes Immun. 2011 Jun;12(4):314-8. PMID: 21390051
We fine map the TAGAP locus in RA.
View article PDF
Genetic overlap of celiac and RA
February 2011
Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies in Celiac Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Identifies Fourteen Non-HLA Shared Loci. Zhernakova A, Stahl EA, Trynka G, Raychaudhuri S, Festen EA, Franke L, Westra HJ, Fehrmann RS, Kurreeman FA, Thomson B, Gupta N, Romanos J, McManus R, Ryan AW, Turner G, Brouwer E, Posthumus MD, Remmers EF, Tucci F, Toes R, Grandone E, Mazzilli MC, Rybak A, Cukrowska B, Coenen MJ, Radstake TR, van Riel PL, Li Y, de Bakker PI, Gregersen PK, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Klareskog L, Huizinga TW, Wijmenga C, Plenge RM. PLoS Genet. 2011 Feb;7(2):e1002004. Epub 2011 Feb 24
We leverage genetic overlap between RA and celiac disease to identify novel loci for both diseases.
View article PDF
Genetic studies in EMR cohort
January 2011
Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records. Kurreeman F, Liao K, Chibnik L, Hickey B, Stahl E, Gainer V, Li G, Bry L, Mahan S, Ardlie K, Thomson B, Szolovits P, Churchill S, Murphy SN, Cai T, Raychaudhuri S, Kohane I, Karlson E, Plenge RM. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;88(1):57-69. PMID: 21211616
We use our i2b2 samples to demonstrate that most RA risk alleles are shared across individuals of distinct geographic ancestry. We also show that a GRS in samples derived from EMR data is identical to a GRS from traditional cohorts.
View article PDF
The Brigham Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS) registry
January 2011
Using genetic and clinical data to understand response to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug therapy: data from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study. Iannaccone CK, Lee YC, Cui J, Frits ML, Glass RJ, Plenge RM, Solomon DH, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA Rheumatology 2011 Jan;50(1):40-6. PMID: 20847201
This manuscript describes the BRASS cohort, which we use in our genetic studies of response to therapy in RA.
View article PDF
Genetics of HIV
December 2010
The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. International HIV Controllers Study. Science 2010 Dec 10;330(6010):1551-7. PMID: 21051598
This represents a large GWAS on HIV elite controllers. Further, it describes for the first time a novel method of HLA amino acid imputation.
View article PDF
Genetic risk of RA in African Americans
December 2010
Most common single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with rheumatoid arthritis in persons of European ancestry confer risk of rheumatoid arthritis in African Americans. Hughes LB, Reynolds RJ, Brown EE, Kelley JM, Thomson B, Conn DL, Jonas BL, Westfall AO, Padilla MA, Callahan LF, Smith EA, Brasington RD, Edberg JC, Kimberly RP, Moreland LW, Plenge RM, Bridges SL Jr. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(12):3547-53. PMID: 21120996
Led by Drs. Laura Hughes, Lou Bridges and colleages from CLEAR, we found that RA risk alleles discovered among individuals of European ancestry also contribute to risk in African Americans, thereby providing support for multi-ethnic approaches to discover new RA risk loci.
View article PDF
Chronic fatigue in i2b2
November 2010
Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus prevalence in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome or chronic immunomodulatory conditions. Henrich TJ, Li JZ, Felsenstein D, Kotton CN, Plenge RM, Pereyra F, Marty FM, Lin NH, Grazioso P, Crochiere DM, Eggers D, Kuritzkes DR, Tsibris AM. J Infect Dis. 2010 Nov 15;202(10):1478-81. PMID: 20936980
We used i2b2 samples to show that XMLV-related virus was not associated with chronic fatigue syndrome.
View article PDF
i2b2 EMR algorithm for RA
August 2010
Electronic medical records for discovery research in rheumatoid arthritis. Liao KP, Cai T, Gainer V, Goryachev S, Zeng-Treitler Q, Raychaudhuri S, Szolovits P, Churchill S, Murphy S, Kohane I, Karlson EW, Plenge RM. Arthritis Care Res. 2010 Aug;62(8):1120-7. PMID: 20235204
This manuscript, the first to come out of our i2b2 project, describes how we mined EMR data to define a virtual cohort of RA patients at Partners HealthCare.
View article PDF
PTPRC gene and response to anti-TNF therapy
July 2010
PTPRC rheumatoid arthritis risk allele is also associated with response to anti-TNF therapy. Cui J, Saevarsdottir S, Thomson B, Padyukov L, van der Helm-van Mil AH, Nititham J, Hughes LB, de Vries N, Raychaudhuri S, Alfredsson L, Askling J, Wedrén S, Ding B, Guiducci C, Wolbink GJ, Crusius JB, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Herenius M, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Worthington J, Batliwalla F, Kern M, Morgan AW, Wilson AG, Isaacs JD, Hyrich K, Seldin MF, Moreland LW, Behrens TW, Allaart CF, Criswell LA, Huizinga TW, Tak PP, Bridges SL Jr, Toes RE, Barton A, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Karlson EW, Plenge RM. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jul;62(7):1849-61. PMID: 20309874
We examined RA risk SNPs for evidence of association to response to anti-TNF therapy. We found suggestive evidence that one SNP in the PTPRC gene (aka CD45) influenced both phenotypes.
View article PDF
Genetic risk scores in RA
June 2010
Cumulative association of 22 genetic variants with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis risk. Karlson EW, Chibnik LB, Kraft P, Cui J, Keenan BT, Ding B, Raychaudhuri S, Klareskog L, Alfredsson L, Plenge RM. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jun;69(6):1077-85. PMID: 20233754
This manuscript represents one of the first application of a genetic risk score (GRS) in RA – aggregating all known risk alleles into a single test of association.
View article PDF
GWAS of RA risk
June 2010
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP, Li Y, Kurreeman FA, Zhernakova A, Hinks A, Guiducci C, Chen R, Alfredsson L, Amos CI, Ardlie KG; BIRAC Consortium, Barton A, Bowes J, Brouwer E, Burtt NP, Catanese JJ, Coblyn J, Coenen MJ, Costenbader KH, Criswell LA, Crusius JB, Cui J, de Bakker PI, De Jager PL, Ding B, Emery P, Flynn E, Harrison P, Hocking LJ, Huizinga TW, Kastner DL, Ke X, Lee AT, Liu X, Martin P, Morgan AW, Padyukov L, Posthumus MD, Radstake TR, Reid DM, Seielstad M, Seldin MF, Shadick NA, Steer S, Tak PP, Thomson W, van der Helm-van Mil AH, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van der Schoot CE, van Riel PL, Weinblatt ME, Wilson AG, Wolbink GJ, Wordsworth BP; YEAR Consortium, Wijmenga C, Karlson EW, Toes RE, de Vries N, Begovich AB, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Gregersen PK, Klareskog L, Plenge RM. Nat Genet. 2010 Jun;42(6):508-14. PMID: 20453842
We conducted a GWAS meta-analysis, leading to the discovery of 7 new RA risk loci. At the time, this was the largest GWAS of RA risk published to date.
View article PDF
GRAIL and GWAS of RA risk
December 2009
Genetic variants at CD28, PRDM1, and CD2/CD58 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis risk. Raychaudhuri S, Thomson BP, Remmers EF, Eyre S, Hinks A, Guiducci C, Catanese JJ, Xie G, Stahl EA, Chen R, Alfredsson L, Amos CI, Ardlie KG; BIRAC Consortium, Barton A, Bowes J, Burtt NP, Chang M, Coblyn J, Costenbader KH, Criswell LA, Crusius JB, Cui J, De Jager PL, Ding B, Emery P, Flynn E, Harrison P, Hocking LJ, Huizinga TW, Kastner DL, Ke X, Kurreeman FA, Lee AT, Liu X, Li Y, Martin P, Morgan AW, Padyukov L, Reid DM, Seielstad M, Seldin MF, Shadick NA, Steer S, Tak PP, Thomson W, van der Helm-van Mil AH, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Weinblatt ME, Wilson AG, Wolbink GJ, Wordsworth P; YEAR Consortium, Altshuler D, Karlson EW, Toes RE, de Vries N, Begovich AB, Siminovitch KA, Worthington J, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Daly MJ, Plenge RM Nat Genet. 2009 Dec;41(12):1313-8. PMID: 19898481
We used GRAIL to prioritize SNPs for replication, leading to the discovery 3 new RA risk loci.
View article PDF
TNFAIP3 and risk of lupus
September 2009
Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Graham RR, Cotsapas C, Davies L, Hackett R, Lessard CJ, Leon JM, Burtt NP, Guiducci C, Parkin M, Gates C, Plenge RM, Behrens TW, Wither JE, Rioux JD, Fortin PR, Graham DC, Wong AK, Vyse TJ, Daly MJ, Altshuler D, Moser KL, Gaffney PM. Nat Genet. 2009 Sep;40(9):1059-61. PMID: 19165918
Led by Dr. Rob Graham, we found that genetic variation at the TNFAIP3 locus contributes to risk of SLE, but in a manner that is different than in RA.
View article PDF
CNVs in Tetrology of Fallot
August 2009
De novo copy number variants identify new genes and loci in isolated sporadic tetralogy of Fallot. Greenway SC, Pereira AC, Lin JC, DePalma SR, Israel SJ, Mesquita SM, Ergul E, Conta JH, Korn JM, McCarroll SA, Gorham JM, Gabriel S, Altshuler DM, Quintanilla-Dieck Mde L, Artunduaga MA, Eavey RD, Plenge RM, Shadick NA, Weinblatt ME, De Jager PL, Hafler DA, Breitbart RE, Seidman JG, Seidman CE. Nat Genet. 2009 Aug;41(8):931-5. PMID: 19597493
Led by our colleagues in the Seidman labs, this paper used GWAS data from the Affy 6.0 array to search for CNVs associated with Tetralogy of Fallot.
View article PDF
GWAS identfies REL
July 2009
REL, encoding a member of the NF-kappaB family of transcription factors, is a newly defined risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis. Gregersen PK, Amos CI, Lee AT, Lu Y, Remmers EF, Kastner DL, Seldin MF, Criswell LA, Plenge RM, Holers VM, Mikuls TR, Sokka T, Moreland LW, Bridges SL Jr, Xie G, Begovich AB, Siminovitch KA. Nat Genet. 2009 Jul;41(7):820-3. PMID: 19503088.
This was the first GWAS to show that a common allele near the c-REL gene influences risk of RA.
View article PDF
The GRAIL manuscript
June 2009
Identifying Relationships Among Genomic Disease Regions: Predicting Genes at Pathogenic SNP Associations and Rare Deletions. Raychaudhuri S, Plenge RM, Rossin EJ, Ng AC; International Schizophrenia Consortium, Purcell SM, Sklar P, Scolnick EM, Xavier RJ, Altshuler D, Daly MJ PLoS Genetics. 2009 Jun;5(6):e1000534. PMID: 19557189.
The is the “GRAIL” paper – we demonstrate the utility of text-mining of published abstracts to establish connections across risk loci implicated in GWAS.
View article PDF
GWAS of CCP titers in RA
May 2009
Genome-wide association study of determinants of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer in adults with rheumatoid arthritis. Cui J, Taylor KE, Destefano AL, Criswell LA, Izmailova ES, Parker A, Roubenoff R, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Karlson EW. Mol Med. 2009 May-Jun;15(5-6):136-43. PMID: 19287509.
We conducted a GWAS to search for common alleles that influence CCP titer.
View article PDF
Prolactin gene and risk of RA
May 2009
The PRL-1149 G/T polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Lee YC, Raychaudhuri S, Cui J, De Vivo I, Ding B, Alfredsson L, Padyukov L, Costenbader KH, Seielstad M, Graham RR, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Plenge RM, Karlson EW. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 May;60(5):1250-4. PMID: 19404952.
We found suggestive evidence that a polymorphism in the prolactin gene influences risk of RA. Subsequent studies failed to replicate this finding, however.
View article PDF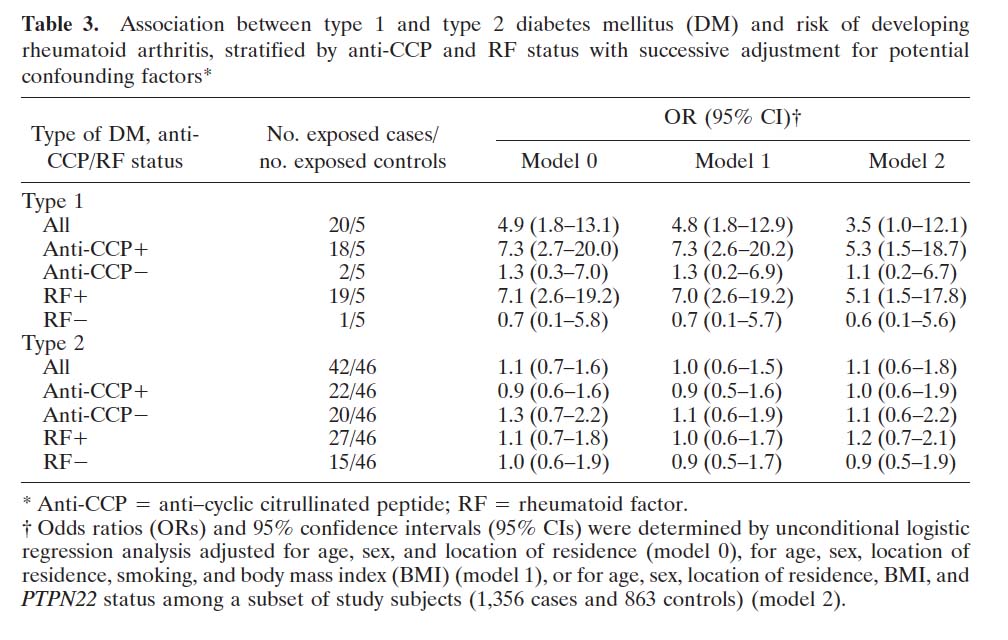
Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes and CCP+ RA
March 2009
Specific association of type 1 diabetes mellitus with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Liao KP, Gunnarsson M, Källberg H, Ding B, Plenge RM, Padyukov L, Karlson EW, Klareskog L, Askling J, Alfredsson L. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Mar;60(3):653-60. PMID: 19248096.
We found that patients with serpositive RA were at an increased risk of type 1 diabetes.
View article PDF
Sex-specific associations in RA
January 2009
The chromosome 7q region association with rheumatoid arthritis in females in a British population is not replicated in a North American case-control series. Korman BD, Seldin MF, Taylor KE, Le JM, Lee AT, Plenge RM, Amos CI, Criswell LA, Gregersen PK, Kastner DL, Remmers EF. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jan;60(1):47-52. PMID: 19116934
This study attempts replication of a previous report for a sex-specific genetic association in risk of RA.
View article PDF
MHC associations in CCP+ vs CCP- RA
January 2009
Different patterns of associations with anti-citrullinated protein antibody-positive and anti-citrullinated protein antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis in the extended major histocompatibility complex region. Ding B, Padyukov L, Lundström E, Seielstad M, Plenge RM, Rioux JD, Gregersen PK, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jan;60(1):30-8. PMID: 19116921
We found that the MHC alleles that contribute to seropositive RA are different from those that contribute to seronegative RA.
View article PDF
HapMap cell lines
November 2008
Genetic Analysis of Human Traits In-Vitro: Drug Response and Gene Expression in Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines. Choy E, Yelensky R, Bonakdar S, Plenge RM, Saxena R, De Jager PL, Shaw SY, Wolfish CS, Slavik JM, Cotsapas C, Rivas M, Dermitzakis ET, Cahir-McFarland E, Kieff E, Hafler D, Daly MJ, and Altshuler D. PLoS Genet. 2008 Nov;4(11):e1000287. PMID: 19043577
We examined whether drug response is heritable in HapMap cell lines.
View article PDF
CD40 and risk of RA
October 2008
Common variants at CD40 and other loci confer risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Hackett R, Guiducci C, Burtt NP, Gianniny L, Korman BD, Padyukov L, Kurreeman FA, Chang M, Catanese JJ, Ding B, Wong S, van der Helm-van Mil AH, Neale BM, Coblyn J, Cui J, Tak PP, Wolbink GJ, Crusius JB, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Criswell LA, Amos CI, Seldin MF, Kastner DL, Ardlie KG, Alfredsson L, Costenbader KH, Altshuler D, Huizinga TW, Shadick NA, Weinblatt ME, de Vries N, Worthington J, Seielstad M, Toes RE, Karlson EW, Begovich AB, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Daly MJ, Plenge RM. Nat Genet. 2008 Oct;40(10):1216-23. PMID: 18794853.
This study represents one of the first GWAS meta-analysis for RA, leading to the discovery of the CD40 risk locus. We have further evaluated CD40 signaling as a drug target.

GWAS of anti-TNF therapy
September 2008
Genome-wide association scan identifies candidate polymorphisms associated with differential response to anti-TNF treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Liu C, Batliwalla F, Li W, Lee A, Roubenoff R, Beckman E, Khalili H, Damle A, Kern M, Plenge RM, Coenen M, Behrens TW, Furie R, Carulli JP, Gregersen PK. Mol Med. 2008 Sep-Oct;14(9-10):575-81. PMID: 18615156
This is a small GWAS of response to anti-TNF therapy in RA. Nonetheless, it set the stage for future GWAS.
View article PDF
Functional studies of CD40 polymorphism
September 2008
A Novel Polymorphism of the Human CD40 Receptor with Enhanced Function. Peters AL, Plenge RM, Graham RR, Altshuler DM, Moser KL, Gaffney PM, and Bishop GA. Blood 2008 Sep 1;112(5):1863-71. PMID: 18591382
We examined the functional consequences of a CD40 polymorphism present at high-frequency among individuals of Native American ancestry.
View article PDF
IL1 genetics and RA
July 2008
A Broad Analysis of IL1 Polymorphism and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Johnsen AK, Plenge RM, Butty V, Campbell C, Dieguez-Gonzalez R, Gomez-Reino JJ, Shadick N, Weinblatt M, Gonzalez A, Gregersen PK, Benoist C, and Mathis D. Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Jul;58(7):1947-57. PMID: 18576312
A promising candidate gene based on studies in mouse and man, we demonstrate that common alleles in the IL1 gene do not contribute to risk of RA.
View article PDF
Genes and the environment in RA
May 2008
Genetic Polymorphisms and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Two Longitudinal Cohort Studies: Evidence of Gene-Environment Interactions with Heavy Cigarette Smoking. Costenbader KH, Chang S, De Vivo I, Plenge R and Karlson EW. Arth Res Ther. 2008;10(3):R52. PMID: 18462498
We provide evidence for gene-environment interactions in conferring risk of RA.
View article PDF
Genetic subsets of lupus
May 2008
Specificity of the STAT4 Genetic Association for Severe Disease Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Taylor KE, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Ortmann WA, Plenge RM, Tian C, Chung SA, Nititham J, Hom G, Kao AH, Demirci FY, Kamboh MI, Petri M, Manzi S, Kastner DL, Seldin MF, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW, Criswell LA. PLoS Genet. 2008 May;4(5):e1000084. PMID: 18516230
We examined genotype-phenotype relationships in patients with SLE.
View article PDF
MHC and risk of RA
May 2008
Several regions in the major histocompatibility complex confer risk for anti-CCP- antibody positive rheumatoid arthritis, independent of the DRB1 locus. Lee HS, Lee AT, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Amos CI, Carulli JP, Navarrete C, Remmers EF, Kastner DL, Plenge RM, Li W, Gregersen PK.Mol Med. 2008 May-Jun;14(5-6):293-300. PMID: 18309376
This study begins to disentangle the different MHC alleles contributing to risk of RA.
View article PDF
MHC and autoimmunity
April 2008
Defining the role of the MHC in autoimmunity: a review and pooled analysis. Fernando MM, Stevens CR, Walsh EC, De Jager PL, Goyette P, Plenge RM, Vyse TJ, Rioux JD. PLoS Genet. 2008 Apr 25;4(4):e1000024. PMID: 18437207
This is a comprehensive evaluation of HLA risk alleles for multiple autoimmune diseases.
View article PDF
Genotype-phenotype correlations in RA
March 2008
Associations between HLA, PTPN22, CTLA4 genotypes and RA phenotypes of autoantibody status, age at diagnosis, and erosions in a large cohort study. Karlson EW, Chibnik LB, Cui J, Plenge RM, Glass RJ, Maher NE, Parker A, Roubenoff R, Izmailova E, Coblyn JS, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Mar;67(3):358-63. PMID: 17666451
This is a study that describes genotype-phenotype correlations for RA risk alleles.
View article PDF
Principal Components Analysis in GWAS
January 2008
Analysis and application of European genetic substructure using 300K SNP information. Tian C, Plenge RM, Ransom M, Lee A, Villoslada P, Selmi C, Klareskog L, Pulver AE, Qi L, Gregersen PK, and Seldin MF. PLoS Genet. 2008 Jan;4(1):e4. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040004. PMID: 18208329
This is an extension of principal components analysis among individuals of European ancestry, demonstrating a genetic distinction between individuals of Northern vs Southern European ancestry.
View article PDF
100K SNP GWAS of RA
December 2007
Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Plenge RM, Cotsapas C, Davies L, Price AL, de Bakker PIW, Maller J, Pe’er I, Burtt NP, Blumenstiel B, DeFelice M, Parkin M, Barry R, Winslow W, Healy C, Graham RR, Izmailova E, Roubenoff R, Parker AN, Coblyn J, Weinblatt ME, Glass R, Karlson EW, Maher N, Hafler DA, Lee DM, Brenner MB, Seldin MF, Remmers EF, Lee AT, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L, Gabriel SB, Purcell S, Klareskog L, Gregersen PK, Shadick NA, Daly MJ, and Altshuler D. Nat Genet. 2007 Dec;39(12):1477-82. PMID: 17982456
This is one of the first GWAS to use “shared controls” to improve statistical power. It was also one of the first to identify independent common alleles influencing risk of one disease (RA).
View article PDF
Discovery of TRAF1-C5 locus in RA
September 2007
TRAF1-C5 as a risk locus for Rheumatoid Arthritis – a genomewide study. Plenge RM*, Seielstad M*, Padyukov L, Lee AT, Remmers EF, Ding B, Liew A, Khalili H, Chandrasekaran A, Davies LRL, Li W, Tan AKS, Bonnard C, Ong RTH, Thalamuthu A, Pettersson S, Liu C, Tian C, Chen WV, Carulli J, Beckman EM, Altshuler D, Alfredsson L, Criswell LA, Amos CI, Seldin MF, W, Kastner DA, Klareskog L, and Gregersen PK New Eng J Med. 2007 Sep 20;357(12):1199-209. PMID: 17804836 *contributed equally
This is one of the first GWAS for RA risk, leading to the identification of the TRAF1-C5 locus.
View article PDF
Discovery of STAT4 in RA and lupus
September 2007
STAT4 and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Remmers EF*, Plenge RM*, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW, de Bakker PIW, Le JM, Lee H, Batliwalla F, Li W, Masters SL, Booty MG, Carulli JP, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L, Chen WV, Amos CI, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Kastner DL, and Gregersen PK New Eng J Med. 2007 Sep 6;357(10):977-86. PMID: 17804842 *contributed equally
This represents one of the first large-scale genetic studies demonstrating that common alleles influence risk of two distinct autoimmune diseases (RA and SLE). We used Tagger to impute the associated STAT4 variant.
View article PDF
Interactions between genes and the environment
May 2007
Gene-Gene and Gene-Environment Interactions Involving HLA-DRB1, PTPN22, and Smoking in Two Subsets of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Kallberg H, Padyukov L, Plenge RM, Ronnelid J, Gregersen PK, van der Helm-van Mil AH, Toes RE, Huizinga TW, Klareskog L, Alfredsson L Am J Hum Genet. 2007 May;80(5):867-75. PMID: 17436241
We provide evidence for gene-gene and gene-environment interactions for risk of RA.
View article PDF
IRF5 and lupus
April 2007
Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Graham RR, Kyogoku C, Sigurdsson S, Vlasova IA, Davies LRL, Baechler EC, Plenge RM, Koeuth T, Ortmann WA, Hom G, Bauer JW, Gillett C, Burtt N, Cunninghame G, Onofrio R, Petri M, Gunnarsson I, Svenungsson E, Ronnblom L, Nordmark G, Gregersen PK, Moser K, Gaffney PM, Criswell LA, Vyse TJ, Syvanen A, Bohjanen PR, Daly MJ, Behrens TW, Altshuler D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007 Apr 17;104(16):6758-63. PMID: 17412832
Led by Dr. Rob Graham and colleagues, we further dissected genotype-phenotype correlations at the IRF5 gene locus.
View article PDF
Skewed X chromosome inactivation
September 2006
X chromosome-inactivation patterns of 1005 phenotypically unaffected females. Amos-Landgraf JM, Cottle A, Plenge RM, Friez M, Schwartz CE, Longshore J, Willard HF. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Sep;79(3):493-9. PMID: 16909387
The most comprehensive study published to date describing variation in X inactivation patterns in the human population.
View article PDF
The EIGENSTRAT manuscript
August 2006
Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D. Nat Genet. 2006 Aug;38(8):904-9. PMID: 16862161
This is the “Eigenstrat” paper – the first study to describe principal components analysis for human GWAS.
View article PDF
IRF5 and lupus
May 2006
A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MVPL, Plenge RM, Bauer JW, Ortmann WA, Koeuth T, Escribano MFG, The Argentine and Spanish Collaborative Groups, Pons-Estel B, Petri M, Daly M, Gregersen PK, Martín J, Altshuler D, Behrens TW, & Alarcón-Riquelme ME. Nat Genet. 2006 May;38(5):550-5. PMID: 16642019
We replicated a previous associated at the IRF5 gene locus, and went on to demonstrate the mechanism of the risk allele (splicing and expression).
View article PDF
Genetic studies in isolated populations
February 2006
Evaluating potential for whole-genome studies in Kosrae, an isolated population in Micronesia. Bonnen PE, Pe’er I, Plenge RM, Salit J, Lowe JK, Shapero MH, Lifton RP, Breslow JL, Daly MJ, Reich DE, Jones KW, Stoffel M, Altshuler D, Friedman JM. Nat Genet. 2006 Feb;38(2):214-7. PMID: 16429162
We examined patterns of linkage disequilibrium (LD) in an isolated population, and found evidence for larger blocks of LD compared to the general population.
View article PDF

Replication, replication, replication
December 2005
Replication of putative candidate gene associations with rheumatoid arthritis in over 4,000 samples from North America and Sweden: association of susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4 and PADI4. Plenge RM, Padyukov L, Remmers EF, Purcell S, Lee AT, Karlson EW, Wolfe F, Kastner DL, Alfredsson L, Altshuler D, Gregersen PK, Klareskog L, Rioux JD. Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Dec;77(6):1044-60. PMID: 16380915
We attempted replication of all previously reported SNP associations with RA risk, and found that only 3 genes (PTPN22, CTLA4, PADI4) consistently showed evidence of association in a large sample collection.
View article PDF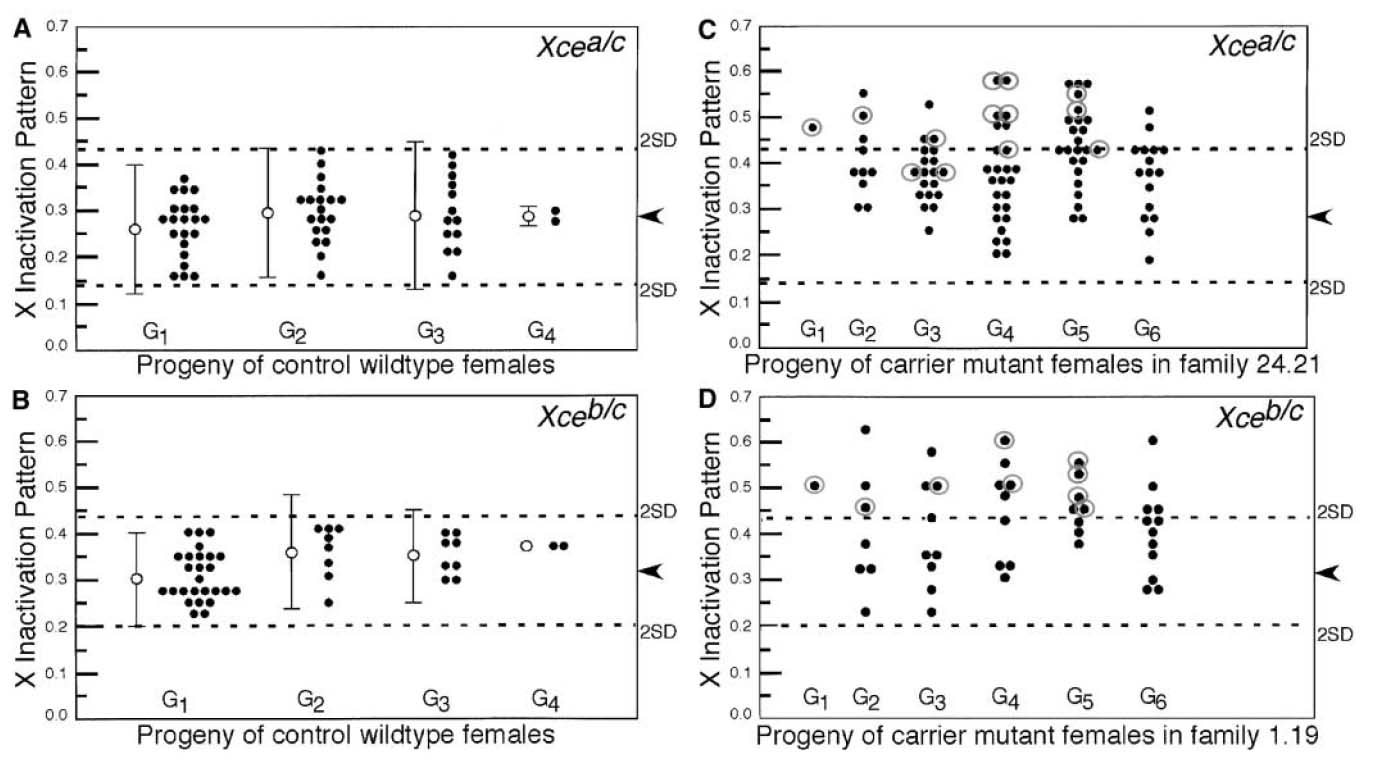
ENU mutagenesis
August 2003
An N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea mutagenesis screen for epigenetic mutations in the mouse. Percec I, Thorvaldsen JL, Plenge RM, Krapp CJ, Nadeau JH, Willard HF, Bartolomei MS. Genetics 2003 Aug;164(4):1481-94. PMID: 12930754
This study provides a more complete description of our ENU mutagenesis in the mouse.
View article PDF

X-linked mental retardation and cell growth
July 2002
Skewed X chromosome inactivation is a common feature of X-linked mental retardation disorders. Plenge RM, Stevenson RA, Lubs HA, Schwartz C, Willard HF. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Jul;71(1):168-73. PMID: 12068376
We found that many X-linked mutations that cause mental retardation (MR) also cause secondary skewed X inactivation in peripheral blood cells, suggesting that MR genes might influence cell proliferation.
View article PDF
X chromosome inactivation mutations
May 2002
Autosomal dominant mutations affecting X inactivation choice in the mouse. Percec I, Plenge RM, Nadeau JH, Bartolomei MS, Willard HF. Science 2002 May 10;296(5570):1136-9. PMID: 12004136
We conducted an ENU mutagenesis screen in the mouse and identified an autosomal locus that, when mutated, influenced the choice of which X chromosome was inactivated.
View article PDF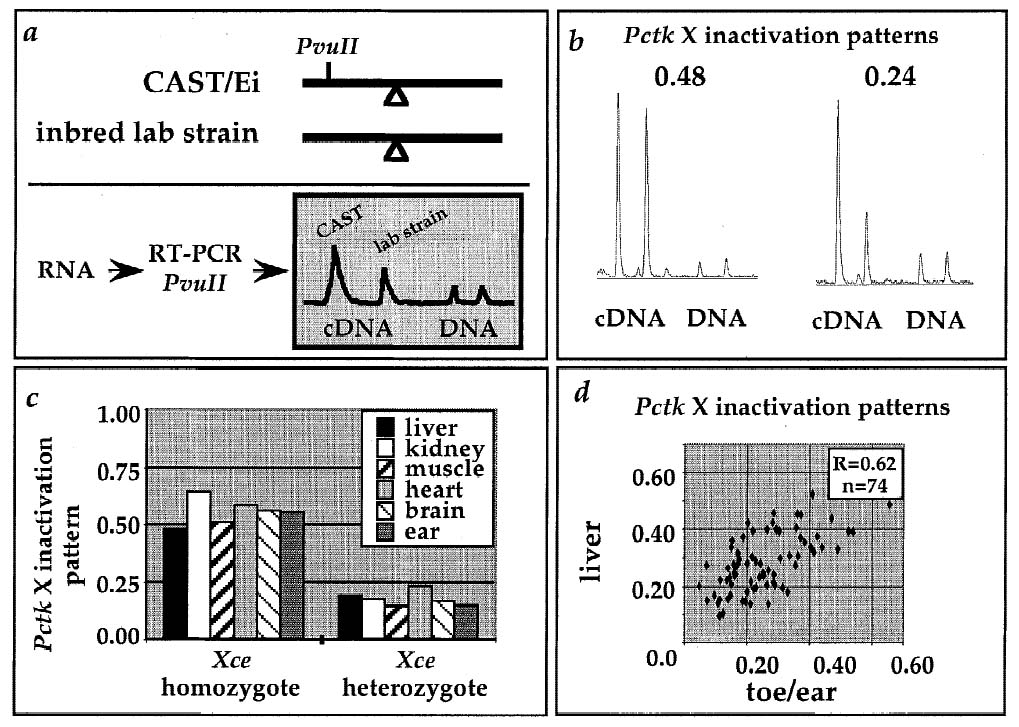
X inactivation assay
May 2000
Expression-based assay of an X-linked gene to examine effects of the X-controlling element (Xce) locus. Plenge RM, Percec I, Nadeau J, Willard HF. Mamm Genome 2000 May;11(5):405-8. PMID: 10790543
We developed a high-throughput expression assay to measure skewed X inactivation in the mouse.
View article PDF
Secondary selection and skewed X inactivation
March 1999
Evidence that mutations in the X-linked DDP gene cause incompletely penetrant and variable skewed X inactivation. Plenge RM, Tranebjaerg L, Schwartz C, Willard HF. Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Mar;64(3):759-67. PMID: 10053010
We found that mutations in a gene, DDP, caused skewed X inactivation through a mechanism of cell selection (occurs after one of the two X chromosomes is randomly chosen).
View article PDF
XIST mutations and skewed X inactivation
November 1997
A promoter mutation in the XIST gene in two unrelated families with skewed X chromosome inactivation. Plenge RM, Hendrich BD, Schwartz C, Arena JF, Naumova A, Sapienza C, Winter RM, Willard HF. Nat Genet. 1997 Nov;17(3):353-6. PMID: 9354806
We identified a rare point mutation that influenced which of the two X chromosomes was chosen to be inactivated in two families. On a personal note, this finding started Robert Plenge’s journey into population genetics and human phenotypes, thanks to Hunt Willard and Aravinda Chakravarti.
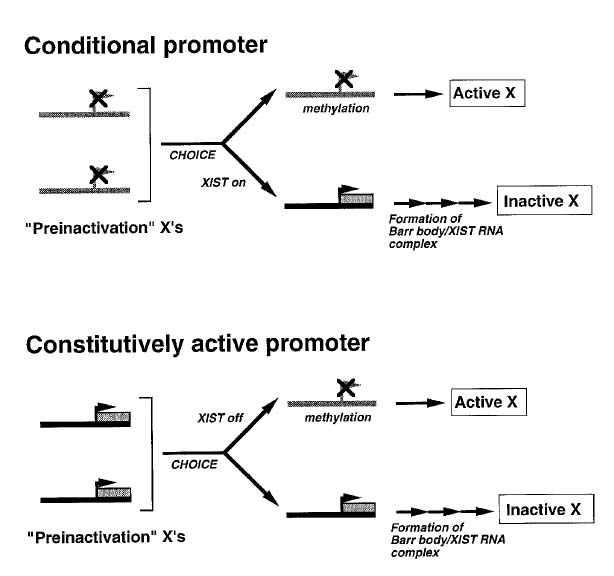
The XIST gene promoter
July 1997
Identification and characterization of the human XIST gene promoter: implications for models of X chromosome inactivation. Hendrich BH, Plenge RM, Willard HF. Nuc Acids Res. 1997 Jul 1;25(13):2661-71. PMID: 9185579
This is a functional study of the human XIST gene, which controls the process of X chromosome inactivation.

X chromosome inactivation
June 1996
Heritability of X chromosome inactivation in a large family. Naumova AK, Plenge RM, Bird LM, Leppert M, Morgan K, Willard HF, Sapienza C. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;58(6):1111-9. PMID: 8651287
This is a family-based study to examine the inheritance of skewed X chromosome inactivation.
View article PDF




